5 Reasons Why Flexibility is the Future of Manufacturing


Ayhan Akyüz
•
Sep 11, 2025
Articles
5 Reasons Why Flexibility is the Future of Manufacturing


Ayhan Akyüz
•
Sep 11, 2025
Articles
5 Reasons Why Flexibility is the Future of Manufacturing


Ayhan Akyüz
•
Sep 11, 2025
Articles
The pharmaceutical industry is experiencing a fundamental transformation. As personalized medicine reshapes treatment paradigms and regulatory demands intensify, traditional manufacturing approaches are proving inadequate. The era of rigid, product-specific automation systems is giving way to a new paradigm: modular automation that prioritizes flexibility, scalability, and rapid adaptation.
This shift isn’t merely a technological upgrade - it’s a strategic imperative for pharmaceutical companies seeking to remain competitive in an era defined by personalized medicine, regulatory complexity, and operational efficiency demands. Let’s explore why modular automation represents the future of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Reason 1: Enhanced Manufacturing Flexibility: Adapting to Personalized Medicine
The pharmaceutical landscape has fundamentally shifted toward personalized therapies tailored to specific genetic profiles and patient subgroups. This transformation necessitates production systems that can handle multiple products with varying formulations, batch sizes, and packaging requirements - a stark departure from traditional blockbuster drug manufacturing.
Traditional automation systems, designed around specific products, struggle with this new reality. They typically require extensive format parts, lengthy changeover procedures, and specialized tooling for each product variant, resulting in high costs and limited flexibility.
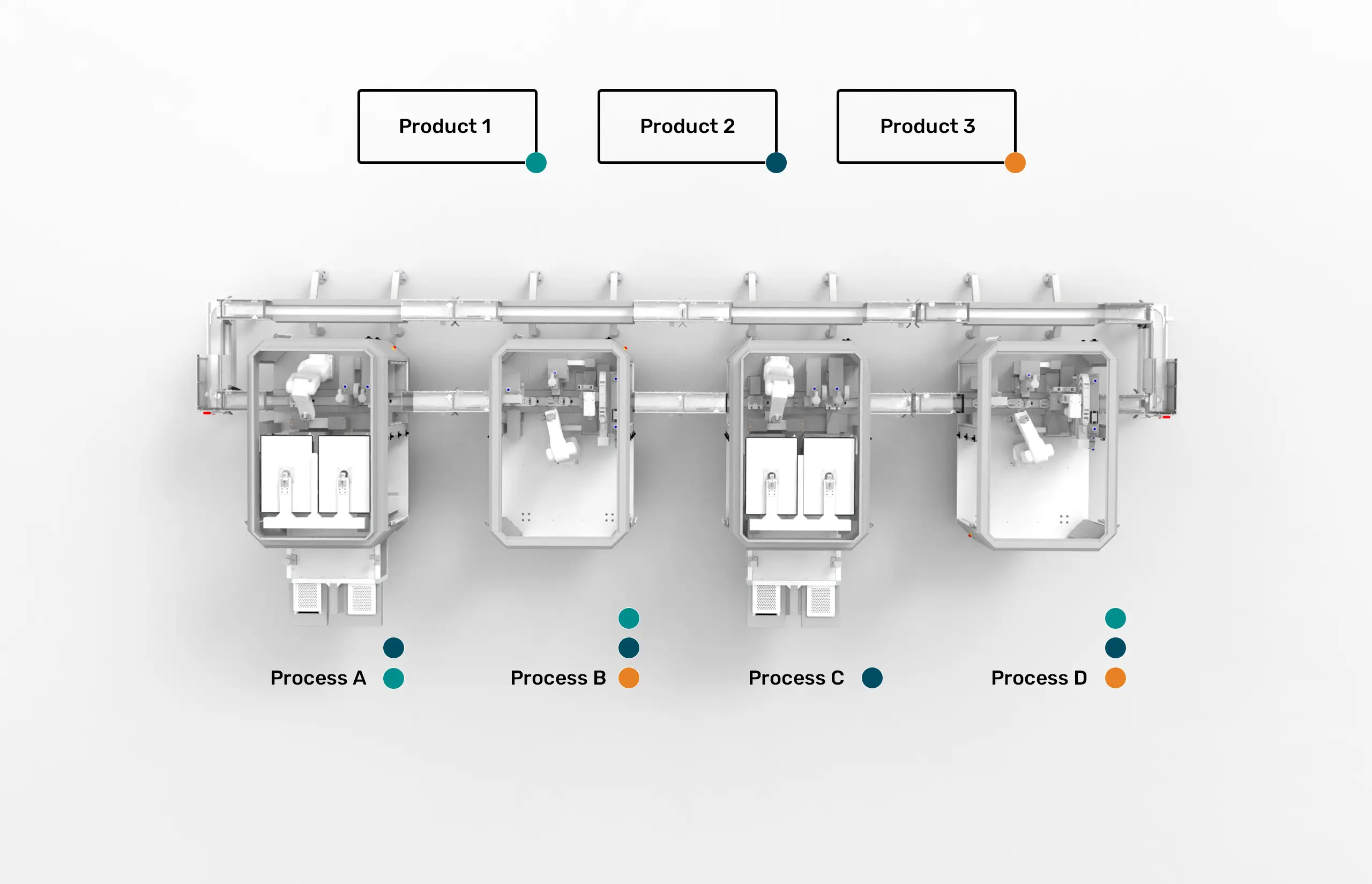
Modular automation addresses these challenges by focusing on process standardization rather than product-specific optimization. The core principle is elegantly simple: instead of designing systems around specific products, modular automation recognizes that pharmaceutical manufacturing consists of a limited set of fundamental processes—filling, capping, labeling, inspection, and packaging.
The ESSERT MicroFactory Ecosystem exemplifies this philosophy through its “one process, one module” approach. Each automation module excels at a specific manufacturing process while maintaining flexibility to handle variations through software configuration rather than hardware modification. A filling module can accommodate different container sizes and volumes without requiring format parts or extensive changeover procedures.
This approach delivers unprecedented flexibility. Product changeovers that traditionally required hours can now be completed in minutes through software-based reconfiguration. The elimination of format parts reduces both changeover complexity and inventory burden. Most importantly, manufacturers can introduce new products without requiring extensive system redesign or revalidation.
Reason 2: Scalable Implementation – Building Automation Incrementally
One of the most significant barriers to automation adoption has been the traditional “all-or-nothing” approach requiring substantial upfront investment in complete production lines. This creates high barriers to entry and forces organizations to make large capital commitments before understanding their automation needs.
Modular automation fundamentally changes this dynamic by enabling incremental implementation strategies that reduce financial risk while providing clear paths for expansion. Organizations can begin their automation journey by focusing on a single, critical process - perhaps the most challenging operation in their workflow.
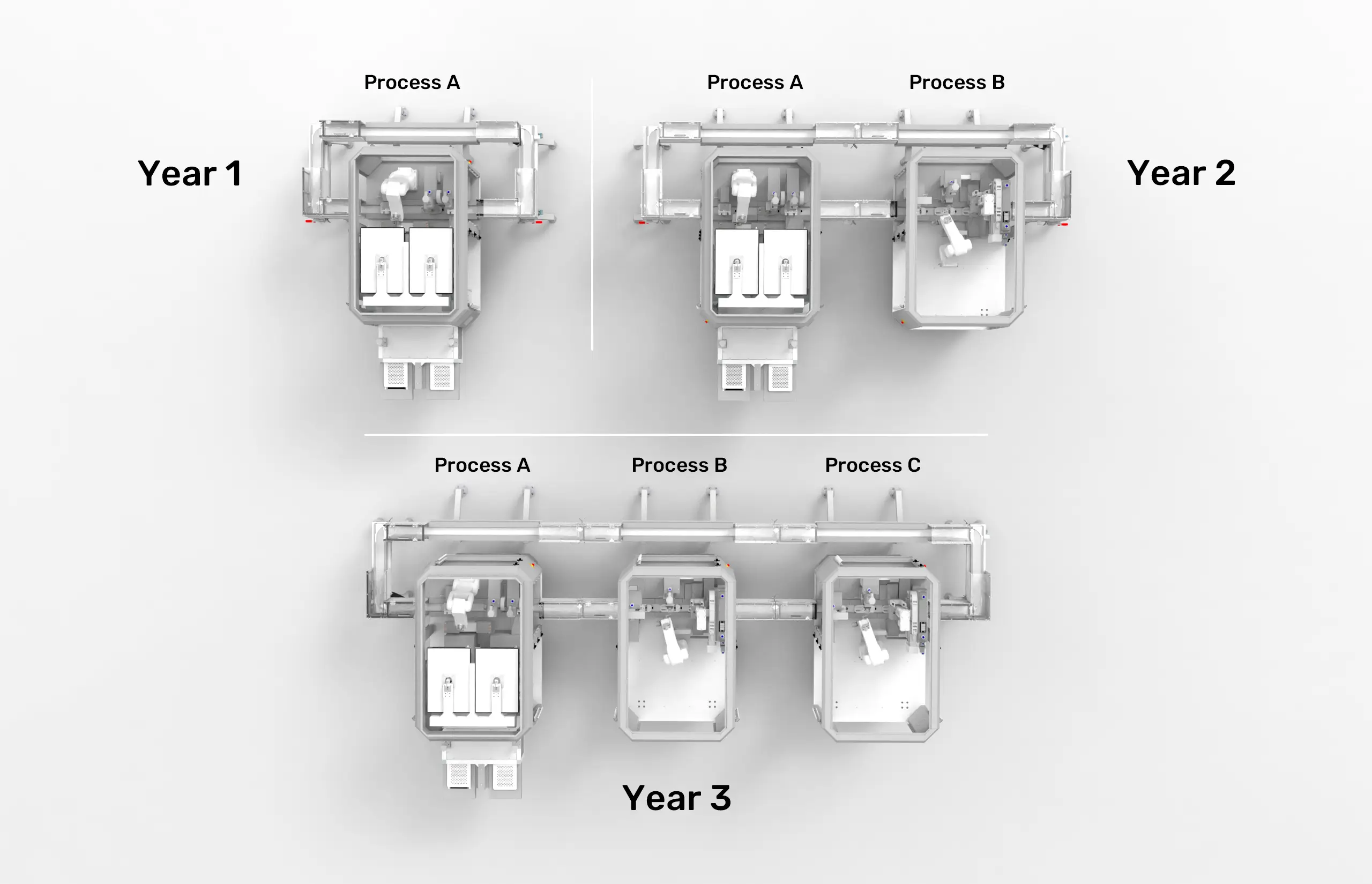
The scalability advantages extend beyond financial considerations. As organizations develop expertise with initial modules, they can strategically expand by adding complementary processes. This organic growth ensures automation expansion aligns with operational experience, market demands, and financial capabilities.
The modular architecture also enables horizontal scaling that traditional systems cannot match. When demand increases, organizations can add parallel modules to increase throughput without disrupting existing operations. This capability proves particularly valuable in pharmaceutical manufacturing, where demand patterns can be unpredictable. The ESSERT MicroFactory platform demonstrates these principles through its standardized base frame architecture and hybrid connector system. Each module provides consistent interfaces while allowing customization for specific applications. The hybrid connectors deliver all necessary utilities - power, air, data, and material transfer - through standardized connection points, enabling rapid reconfiguration and expansion.
Organizations implementing modular automation report significant advantages in managing growth and change. The ability to start small and scale incrementally reduces investment risk while providing flexibility to adapt to evolving requirements.
Reason 3: Reduced Changeover Time – Maximizing Production Efficiency
In modern pharmaceutical manufacturing, the ability to rapidly transition between products has become a critical competitive advantage. Traditional automation systems often require extensive changeover procedures that can consume hours or days of production time, reducing overall equipment effectiveness and limiting manufacturing flexibility.
Modular automation addresses changeover challenges through process-oriented design that minimizes product-specific hardware requirements. Instead of relying on format parts and mechanical adjustments, modular systems achieve product differentiation through software configuration and parameter adjustment, enabling changeovers to be completed in minutes rather than hours.
The changeover time reduction stems from several key design principles. First, standardization of process modules eliminates the need for product-specific tooling. An assembly module designed to handle multiple product types through software-controlled positioning and component selection requires no physical reconfiguration when switching between products.
Second, the modular approach enables parallel changeover activities. While one module is being reconfigured, other modules can continue operating or be prepared for the upcoming changeover, minimizing overall line downtime.
The software-centric nature of modular changeovers also improves consistency and reduces human error. Traditional changeovers often involve complex mechanical adjustments requiring skilled technicians. Modular systems can store product-specific parameters in software recipes that automatically configure all relevant components.
Companies report changeover reductions from several hours to less than minutes, enabling production schedules that would be impossible with traditional systems. This improvement allows manufacturers to respond more quickly to market demands, reduce inventory requirements, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Reason 4: Simplified Validation and Compliance – Streamlining Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory compliance represents one of the most complex and costly aspects of pharmaceutical manufacturing. Traditional automation systems compound these challenges by requiring comprehensive revalidation whenever modifications are made to accommodate new products or process improvements.
Modular automation fundamentally changes the validation paradigm by enabling independent qualification of individual process modules. This modular qualification approach allows each module to be validated separately based on its specific function and operating parameters. Once qualified, modules can be combined with other qualified modules without affecting existing validation status.
The modular qualification approach offers several significant advantages. First, it reduces the scope and complexity of individual validation activities. Instead of validating an entire production line, organizations can focus on specific process modules, making validation more manageable and less resource-intensive.
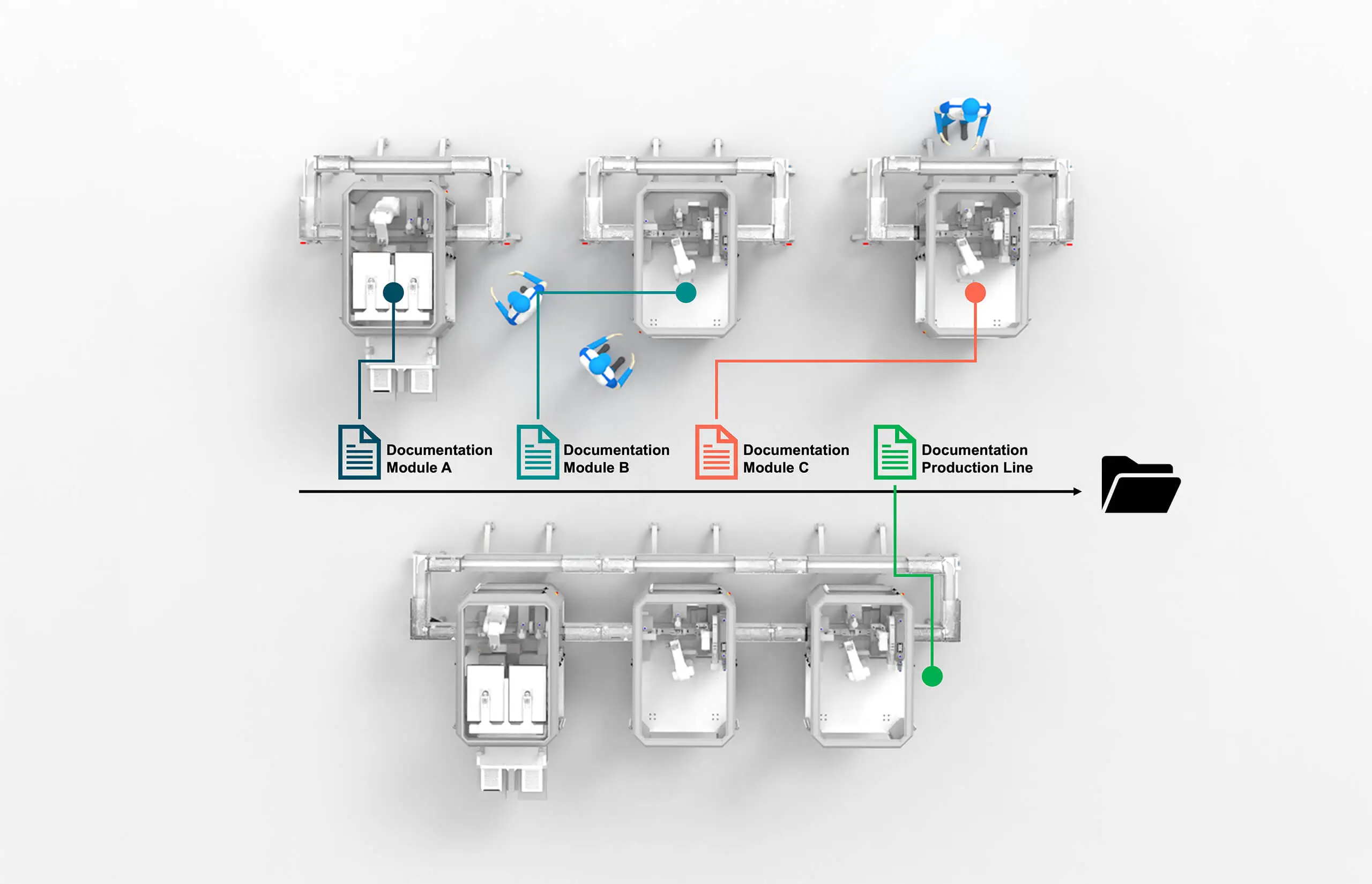
Second, modular qualification enables faster implementation of system modifications. When organizations need to add capabilities or modify processes, they can qualify new modules independently without affecting existing validated systems, significantly reducing time and cost.
The standardized nature of modular systems also simplifies validation by enabling reusable validation protocols and documentation. Once a particular module type has been validated, similar modules can leverage existing validation work, reducing effort for subsequent implementations.
ESSERT’s approach to modular qualification includes comprehensive documentation packages that support independent module validation. Each MicroFactory module includes detailed specifications, operating procedures, and validation protocols that enable efficient qualification activities.
Organizations implementing modular automation report significant improvements in managing regulatory requirements. The reduced validation burden enables faster implementation of process improvements and new product introductions while maintaining compliance standards.
Reason 5: Improved Return on Investment – Maximizing Automation Value
The financial justification for automation investments has become increasingly complex as pharmaceutical companies face pressure to reduce costs while maintaining quality standards. Traditional automation systems, with their high upfront costs and limited flexibility, often struggle to deliver compelling returns on investment.
Modular automation transforms the ROI equation by reducing initial investment requirements while providing superior long-term value through enhanced flexibility and scalability. The incremental implementation approach enables organizations to spread automation investments over time, reducing financial risk while providing opportunities to optimize returns.
The ROI advantages stem from multiple sources. First, reduced initial investment requirements enable faster payback periods and lower financial risk. Organizations can begin realizing automation benefits from their first module while building experience that informs subsequent investments.
Second, enhanced flexibility enables higher asset utilization rates. Traditional systems optimized for specific products often experience significant idle time when demand patterns change. Modular systems can be rapidly reconfigured to accommodate different products, maintaining high utilization rates across diverse operating conditions.
Operational efficiency improvements represent another significant ROI source. Reduced changeover times, improved quality consistency, and enhanced process control translate directly into productivity improvements and cost reductions. Companies implementing modular automation typically report productivity increases of 30-50% compared to manual or traditional automation approaches.
Quality improvements also contribute to ROI through reduced waste, rework, and compliance costs. The precision and repeatability of automated processes significantly reduce product defects and quality variations, resulting in higher yields and lower quality-related costs.
Real-world ROI data demonstrates compelling financial returns. Companies report payback periods ranging from 18 months to 3 years, with ongoing benefits that accumulate over the 10-15 year equipment lifecycle. The combination of direct operational benefits and strategic value creation often results in total returns that significantly exceed initial projections.
The Future is Modular
The transformation of pharmaceutical manufacturing through modular automation represents more than technological evolution - it embodies a fundamental shift in how the industry approaches modern drug production challenges. The five key advantages work synergistically to create manufacturing capabilities that far exceed the sum of their individual benefits.
Organizations that embrace modular automation gain not only operational improvements but also strategic agility that enables them to pursue opportunities and respond to challenges impossible with traditional manufacturing approaches. The evidence from real-world implementations demonstrates that modular automation delivers on its promises across productivity, quality, and operational efficiency metrics.
The path forward requires commitment to change and willingness to invest in new capabilities. Organizations that delay this transformation risk being left behind by more agile competitors who leverage modular automation to pursue market opportunities and operational efficiencies.
For pharmaceutical executives considering automation investments, the evidence strongly supports prioritizing flexibility and modularity over pure efficiency optimization. The traditional approach of optimizing for specific products is increasingly obsolete in a market characterized by product diversity, changing regulations, and unpredictable demand patterns.
The pharmaceutical industry is experiencing a fundamental transformation. As personalized medicine reshapes treatment paradigms and regulatory demands intensify, traditional manufacturing approaches are proving inadequate. The era of rigid, product-specific automation systems is giving way to a new paradigm: modular automation that prioritizes flexibility, scalability, and rapid adaptation.
This shift isn’t merely a technological upgrade - it’s a strategic imperative for pharmaceutical companies seeking to remain competitive in an era defined by personalized medicine, regulatory complexity, and operational efficiency demands. Let’s explore why modular automation represents the future of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Reason 1: Enhanced Manufacturing Flexibility: Adapting to Personalized Medicine
The pharmaceutical landscape has fundamentally shifted toward personalized therapies tailored to specific genetic profiles and patient subgroups. This transformation necessitates production systems that can handle multiple products with varying formulations, batch sizes, and packaging requirements - a stark departure from traditional blockbuster drug manufacturing.
Traditional automation systems, designed around specific products, struggle with this new reality. They typically require extensive format parts, lengthy changeover procedures, and specialized tooling for each product variant, resulting in high costs and limited flexibility.

Modular automation addresses these challenges by focusing on process standardization rather than product-specific optimization. The core principle is elegantly simple: instead of designing systems around specific products, modular automation recognizes that pharmaceutical manufacturing consists of a limited set of fundamental processes—filling, capping, labeling, inspection, and packaging.
The ESSERT MicroFactory Ecosystem exemplifies this philosophy through its “one process, one module” approach. Each automation module excels at a specific manufacturing process while maintaining flexibility to handle variations through software configuration rather than hardware modification. A filling module can accommodate different container sizes and volumes without requiring format parts or extensive changeover procedures.
This approach delivers unprecedented flexibility. Product changeovers that traditionally required hours can now be completed in minutes through software-based reconfiguration. The elimination of format parts reduces both changeover complexity and inventory burden. Most importantly, manufacturers can introduce new products without requiring extensive system redesign or revalidation.
Reason 2: Scalable Implementation – Building Automation Incrementally
One of the most significant barriers to automation adoption has been the traditional “all-or-nothing” approach requiring substantial upfront investment in complete production lines. This creates high barriers to entry and forces organizations to make large capital commitments before understanding their automation needs.
Modular automation fundamentally changes this dynamic by enabling incremental implementation strategies that reduce financial risk while providing clear paths for expansion. Organizations can begin their automation journey by focusing on a single, critical process - perhaps the most challenging operation in their workflow.

The scalability advantages extend beyond financial considerations. As organizations develop expertise with initial modules, they can strategically expand by adding complementary processes. This organic growth ensures automation expansion aligns with operational experience, market demands, and financial capabilities.
The modular architecture also enables horizontal scaling that traditional systems cannot match. When demand increases, organizations can add parallel modules to increase throughput without disrupting existing operations. This capability proves particularly valuable in pharmaceutical manufacturing, where demand patterns can be unpredictable. The ESSERT MicroFactory platform demonstrates these principles through its standardized base frame architecture and hybrid connector system. Each module provides consistent interfaces while allowing customization for specific applications. The hybrid connectors deliver all necessary utilities - power, air, data, and material transfer - through standardized connection points, enabling rapid reconfiguration and expansion.
Organizations implementing modular automation report significant advantages in managing growth and change. The ability to start small and scale incrementally reduces investment risk while providing flexibility to adapt to evolving requirements.
Reason 3: Reduced Changeover Time – Maximizing Production Efficiency
In modern pharmaceutical manufacturing, the ability to rapidly transition between products has become a critical competitive advantage. Traditional automation systems often require extensive changeover procedures that can consume hours or days of production time, reducing overall equipment effectiveness and limiting manufacturing flexibility.
Modular automation addresses changeover challenges through process-oriented design that minimizes product-specific hardware requirements. Instead of relying on format parts and mechanical adjustments, modular systems achieve product differentiation through software configuration and parameter adjustment, enabling changeovers to be completed in minutes rather than hours.
The changeover time reduction stems from several key design principles. First, standardization of process modules eliminates the need for product-specific tooling. An assembly module designed to handle multiple product types through software-controlled positioning and component selection requires no physical reconfiguration when switching between products.
Second, the modular approach enables parallel changeover activities. While one module is being reconfigured, other modules can continue operating or be prepared for the upcoming changeover, minimizing overall line downtime.
The software-centric nature of modular changeovers also improves consistency and reduces human error. Traditional changeovers often involve complex mechanical adjustments requiring skilled technicians. Modular systems can store product-specific parameters in software recipes that automatically configure all relevant components.
Companies report changeover reductions from several hours to less than minutes, enabling production schedules that would be impossible with traditional systems. This improvement allows manufacturers to respond more quickly to market demands, reduce inventory requirements, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Reason 4: Simplified Validation and Compliance – Streamlining Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory compliance represents one of the most complex and costly aspects of pharmaceutical manufacturing. Traditional automation systems compound these challenges by requiring comprehensive revalidation whenever modifications are made to accommodate new products or process improvements.
Modular automation fundamentally changes the validation paradigm by enabling independent qualification of individual process modules. This modular qualification approach allows each module to be validated separately based on its specific function and operating parameters. Once qualified, modules can be combined with other qualified modules without affecting existing validation status.
The modular qualification approach offers several significant advantages. First, it reduces the scope and complexity of individual validation activities. Instead of validating an entire production line, organizations can focus on specific process modules, making validation more manageable and less resource-intensive.

Second, modular qualification enables faster implementation of system modifications. When organizations need to add capabilities or modify processes, they can qualify new modules independently without affecting existing validated systems, significantly reducing time and cost.
The standardized nature of modular systems also simplifies validation by enabling reusable validation protocols and documentation. Once a particular module type has been validated, similar modules can leverage existing validation work, reducing effort for subsequent implementations.
ESSERT’s approach to modular qualification includes comprehensive documentation packages that support independent module validation. Each MicroFactory module includes detailed specifications, operating procedures, and validation protocols that enable efficient qualification activities.
Organizations implementing modular automation report significant improvements in managing regulatory requirements. The reduced validation burden enables faster implementation of process improvements and new product introductions while maintaining compliance standards.
Reason 5: Improved Return on Investment – Maximizing Automation Value
The financial justification for automation investments has become increasingly complex as pharmaceutical companies face pressure to reduce costs while maintaining quality standards. Traditional automation systems, with their high upfront costs and limited flexibility, often struggle to deliver compelling returns on investment.
Modular automation transforms the ROI equation by reducing initial investment requirements while providing superior long-term value through enhanced flexibility and scalability. The incremental implementation approach enables organizations to spread automation investments over time, reducing financial risk while providing opportunities to optimize returns.
The ROI advantages stem from multiple sources. First, reduced initial investment requirements enable faster payback periods and lower financial risk. Organizations can begin realizing automation benefits from their first module while building experience that informs subsequent investments.
Second, enhanced flexibility enables higher asset utilization rates. Traditional systems optimized for specific products often experience significant idle time when demand patterns change. Modular systems can be rapidly reconfigured to accommodate different products, maintaining high utilization rates across diverse operating conditions.
Operational efficiency improvements represent another significant ROI source. Reduced changeover times, improved quality consistency, and enhanced process control translate directly into productivity improvements and cost reductions. Companies implementing modular automation typically report productivity increases of 30-50% compared to manual or traditional automation approaches.
Quality improvements also contribute to ROI through reduced waste, rework, and compliance costs. The precision and repeatability of automated processes significantly reduce product defects and quality variations, resulting in higher yields and lower quality-related costs.
Real-world ROI data demonstrates compelling financial returns. Companies report payback periods ranging from 18 months to 3 years, with ongoing benefits that accumulate over the 10-15 year equipment lifecycle. The combination of direct operational benefits and strategic value creation often results in total returns that significantly exceed initial projections.
The Future is Modular
The transformation of pharmaceutical manufacturing through modular automation represents more than technological evolution - it embodies a fundamental shift in how the industry approaches modern drug production challenges. The five key advantages work synergistically to create manufacturing capabilities that far exceed the sum of their individual benefits.
Organizations that embrace modular automation gain not only operational improvements but also strategic agility that enables them to pursue opportunities and respond to challenges impossible with traditional manufacturing approaches. The evidence from real-world implementations demonstrates that modular automation delivers on its promises across productivity, quality, and operational efficiency metrics.
The path forward requires commitment to change and willingness to invest in new capabilities. Organizations that delay this transformation risk being left behind by more agile competitors who leverage modular automation to pursue market opportunities and operational efficiencies.
For pharmaceutical executives considering automation investments, the evidence strongly supports prioritizing flexibility and modularity over pure efficiency optimization. The traditional approach of optimizing for specific products is increasingly obsolete in a market characterized by product diversity, changing regulations, and unpredictable demand patterns.
The pharmaceutical industry is experiencing a fundamental transformation. As personalized medicine reshapes treatment paradigms and regulatory demands intensify, traditional manufacturing approaches are proving inadequate. The era of rigid, product-specific automation systems is giving way to a new paradigm: modular automation that prioritizes flexibility, scalability, and rapid adaptation.
This shift isn’t merely a technological upgrade - it’s a strategic imperative for pharmaceutical companies seeking to remain competitive in an era defined by personalized medicine, regulatory complexity, and operational efficiency demands. Let’s explore why modular automation represents the future of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Reason 1: Enhanced Manufacturing Flexibility: Adapting to Personalized Medicine
The pharmaceutical landscape has fundamentally shifted toward personalized therapies tailored to specific genetic profiles and patient subgroups. This transformation necessitates production systems that can handle multiple products with varying formulations, batch sizes, and packaging requirements - a stark departure from traditional blockbuster drug manufacturing.
Traditional automation systems, designed around specific products, struggle with this new reality. They typically require extensive format parts, lengthy changeover procedures, and specialized tooling for each product variant, resulting in high costs and limited flexibility.

Modular automation addresses these challenges by focusing on process standardization rather than product-specific optimization. The core principle is elegantly simple: instead of designing systems around specific products, modular automation recognizes that pharmaceutical manufacturing consists of a limited set of fundamental processes—filling, capping, labeling, inspection, and packaging.
The ESSERT MicroFactory Ecosystem exemplifies this philosophy through its “one process, one module” approach. Each automation module excels at a specific manufacturing process while maintaining flexibility to handle variations through software configuration rather than hardware modification. A filling module can accommodate different container sizes and volumes without requiring format parts or extensive changeover procedures.
This approach delivers unprecedented flexibility. Product changeovers that traditionally required hours can now be completed in minutes through software-based reconfiguration. The elimination of format parts reduces both changeover complexity and inventory burden. Most importantly, manufacturers can introduce new products without requiring extensive system redesign or revalidation.
Reason 2: Scalable Implementation – Building Automation Incrementally
One of the most significant barriers to automation adoption has been the traditional “all-or-nothing” approach requiring substantial upfront investment in complete production lines. This creates high barriers to entry and forces organizations to make large capital commitments before understanding their automation needs.
Modular automation fundamentally changes this dynamic by enabling incremental implementation strategies that reduce financial risk while providing clear paths for expansion. Organizations can begin their automation journey by focusing on a single, critical process - perhaps the most challenging operation in their workflow.

The scalability advantages extend beyond financial considerations. As organizations develop expertise with initial modules, they can strategically expand by adding complementary processes. This organic growth ensures automation expansion aligns with operational experience, market demands, and financial capabilities.
The modular architecture also enables horizontal scaling that traditional systems cannot match. When demand increases, organizations can add parallel modules to increase throughput without disrupting existing operations. This capability proves particularly valuable in pharmaceutical manufacturing, where demand patterns can be unpredictable. The ESSERT MicroFactory platform demonstrates these principles through its standardized base frame architecture and hybrid connector system. Each module provides consistent interfaces while allowing customization for specific applications. The hybrid connectors deliver all necessary utilities - power, air, data, and material transfer - through standardized connection points, enabling rapid reconfiguration and expansion.
Organizations implementing modular automation report significant advantages in managing growth and change. The ability to start small and scale incrementally reduces investment risk while providing flexibility to adapt to evolving requirements.
Reason 3: Reduced Changeover Time – Maximizing Production Efficiency
In modern pharmaceutical manufacturing, the ability to rapidly transition between products has become a critical competitive advantage. Traditional automation systems often require extensive changeover procedures that can consume hours or days of production time, reducing overall equipment effectiveness and limiting manufacturing flexibility.
Modular automation addresses changeover challenges through process-oriented design that minimizes product-specific hardware requirements. Instead of relying on format parts and mechanical adjustments, modular systems achieve product differentiation through software configuration and parameter adjustment, enabling changeovers to be completed in minutes rather than hours.
The changeover time reduction stems from several key design principles. First, standardization of process modules eliminates the need for product-specific tooling. An assembly module designed to handle multiple product types through software-controlled positioning and component selection requires no physical reconfiguration when switching between products.
Second, the modular approach enables parallel changeover activities. While one module is being reconfigured, other modules can continue operating or be prepared for the upcoming changeover, minimizing overall line downtime.
The software-centric nature of modular changeovers also improves consistency and reduces human error. Traditional changeovers often involve complex mechanical adjustments requiring skilled technicians. Modular systems can store product-specific parameters in software recipes that automatically configure all relevant components.
Companies report changeover reductions from several hours to less than minutes, enabling production schedules that would be impossible with traditional systems. This improvement allows manufacturers to respond more quickly to market demands, reduce inventory requirements, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Reason 4: Simplified Validation and Compliance – Streamlining Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory compliance represents one of the most complex and costly aspects of pharmaceutical manufacturing. Traditional automation systems compound these challenges by requiring comprehensive revalidation whenever modifications are made to accommodate new products or process improvements.
Modular automation fundamentally changes the validation paradigm by enabling independent qualification of individual process modules. This modular qualification approach allows each module to be validated separately based on its specific function and operating parameters. Once qualified, modules can be combined with other qualified modules without affecting existing validation status.
The modular qualification approach offers several significant advantages. First, it reduces the scope and complexity of individual validation activities. Instead of validating an entire production line, organizations can focus on specific process modules, making validation more manageable and less resource-intensive.

Second, modular qualification enables faster implementation of system modifications. When organizations need to add capabilities or modify processes, they can qualify new modules independently without affecting existing validated systems, significantly reducing time and cost.
The standardized nature of modular systems also simplifies validation by enabling reusable validation protocols and documentation. Once a particular module type has been validated, similar modules can leverage existing validation work, reducing effort for subsequent implementations.
ESSERT’s approach to modular qualification includes comprehensive documentation packages that support independent module validation. Each MicroFactory module includes detailed specifications, operating procedures, and validation protocols that enable efficient qualification activities.
Organizations implementing modular automation report significant improvements in managing regulatory requirements. The reduced validation burden enables faster implementation of process improvements and new product introductions while maintaining compliance standards.
Reason 5: Improved Return on Investment – Maximizing Automation Value
The financial justification for automation investments has become increasingly complex as pharmaceutical companies face pressure to reduce costs while maintaining quality standards. Traditional automation systems, with their high upfront costs and limited flexibility, often struggle to deliver compelling returns on investment.
Modular automation transforms the ROI equation by reducing initial investment requirements while providing superior long-term value through enhanced flexibility and scalability. The incremental implementation approach enables organizations to spread automation investments over time, reducing financial risk while providing opportunities to optimize returns.
The ROI advantages stem from multiple sources. First, reduced initial investment requirements enable faster payback periods and lower financial risk. Organizations can begin realizing automation benefits from their first module while building experience that informs subsequent investments.
Second, enhanced flexibility enables higher asset utilization rates. Traditional systems optimized for specific products often experience significant idle time when demand patterns change. Modular systems can be rapidly reconfigured to accommodate different products, maintaining high utilization rates across diverse operating conditions.
Operational efficiency improvements represent another significant ROI source. Reduced changeover times, improved quality consistency, and enhanced process control translate directly into productivity improvements and cost reductions. Companies implementing modular automation typically report productivity increases of 30-50% compared to manual or traditional automation approaches.
Quality improvements also contribute to ROI through reduced waste, rework, and compliance costs. The precision and repeatability of automated processes significantly reduce product defects and quality variations, resulting in higher yields and lower quality-related costs.
Real-world ROI data demonstrates compelling financial returns. Companies report payback periods ranging from 18 months to 3 years, with ongoing benefits that accumulate over the 10-15 year equipment lifecycle. The combination of direct operational benefits and strategic value creation often results in total returns that significantly exceed initial projections.
The Future is Modular
The transformation of pharmaceutical manufacturing through modular automation represents more than technological evolution - it embodies a fundamental shift in how the industry approaches modern drug production challenges. The five key advantages work synergistically to create manufacturing capabilities that far exceed the sum of their individual benefits.
Organizations that embrace modular automation gain not only operational improvements but also strategic agility that enables them to pursue opportunities and respond to challenges impossible with traditional manufacturing approaches. The evidence from real-world implementations demonstrates that modular automation delivers on its promises across productivity, quality, and operational efficiency metrics.
The path forward requires commitment to change and willingness to invest in new capabilities. Organizations that delay this transformation risk being left behind by more agile competitors who leverage modular automation to pursue market opportunities and operational efficiencies.
For pharmaceutical executives considering automation investments, the evidence strongly supports prioritizing flexibility and modularity over pure efficiency optimization. The traditional approach of optimizing for specific products is increasingly obsolete in a market characterized by product diversity, changing regulations, and unpredictable demand patterns.

Let’s Talk
Automation is a long-term commitment. We partner with manufacturers who think in lifecycles. If you are evaluating automation for a new product, scaling a process, or preparing for a future pipeline - let’s talk.

Let’s Talk
Automation is a long-term commitment. We partner with manufacturers who think in lifecycles. If you are evaluating automation for a new product, scaling a process, or preparing for a future pipeline - let’s talk.

Let’s Talk
Automation is a long-term commitment. We partner with manufacturers who think in lifecycles. If you are evaluating automation for a new product, scaling a process, or preparing for a future pipeline - let’s talk.
See what's new

Automating the Full Blister Line: From Product Loading to Inspection
Ask most Pharma or MedTech production managers where their biggest packaging bottleneck is, and they will point somewhere on the blister line. It might be the manual product loading step, ...

5 Reasons for automated medical device assembly
The assembly of medical devices is often much more complex than the manufacturing of traditional consumer goods. The reasons are ...

The Last Manual Bottleneck in Pharma Manufacturing
The economic impact of manual tub and vial handling extends far beyond visible labor costs. While managers can calculate hourly wages, ...
See what's new

Automating the Full Blister Line: From Product Loading to Inspection
Ask most Pharma or MedTech production managers where their biggest packaging bottleneck is, and they will point somewhere on the blister line. It might be the manual product loading step, ...

5 Reasons for automated medical device assembly
The assembly of medical devices is often much more complex than the manufacturing of traditional consumer goods. The reasons are ...

The Last Manual Bottleneck in Pharma Manufacturing
The economic impact of manual tub and vial handling extends far beyond visible labor costs. While managers can calculate hourly wages, ...
See what's new

Automating the Full Blister Line: From Product Loading to Inspection
Ask most Pharma or MedTech production managers where their biggest packaging bottleneck is, and they will point somewhere on the blister line. It might be the manual product loading step, ...

5 Reasons for automated medical device assembly
The assembly of medical devices is often much more complex than the manufacturing of traditional consumer goods. The reasons are ...

The Last Manual Bottleneck in Pharma Manufacturing
The economic impact of manual tub and vial handling extends far beyond visible labor costs. While managers can calculate hourly wages, ...
Contact our team
From initial questions to your custom MicroFactory solutions – our team is here to assist you.
Contact our team
From initial questions to your custom MicroFactory solutions – our team is here to assist you.
Contact our team
From initial questions to your custom MicroFactory solutions – our team is here to assist you.