9 types of robotics

Robotics has burgeoned into a multifaceted landscape, with a myriad of machines designed to perform tasks across diverse industries. As technology advances, the classification of robots broadens, making it challenging to determine what type a specific robot belongs to.
In this article, we will investigate nine distinctive types of robotics that find widespread use in different fields – from general industries to the life sciences sector.
General classification of robots
The field of robotics encompasses a wide array of machines, each tailored to specific tasks and industries. As there is a huge variety of sometimes even tailor-made robotic solutions available, it is not without challenges to categorize them.
However, three main classes of robotics can be distinguished.
Industrial robots
At the heart of modern manufacturing, industrial robots redefine efficiency. These machines, equipped with advanced sensors and articulated arms, automate tasks with enormous precision.
From automotive assembly lines to semiconductor production, industrial robots optimize processes, reducing costs and enhancing quality. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning elevates their capabilities, allowing for predictive maintenance and adaptive responses in complex production environments.
These environments also include sectors like the pharmaceutical industry, where the production of small volumes with frequently changing parameters is especially challenging. Here, flexible robotic solutions as provided by ESSERT Robotics come into play, allowing to be quickly adapted to altered production lines.

Cobots
Collaborative robots, or cobots, transcend the traditional boundaries between man and machine. Engineered for human-robot collaboration, cobots streamline workflows in sectors demanding precision and human decisions.
In manufacturing, cobots work seamlessly alongside skilled technicians, handling tasks that require a delicate touch, such as specific assembly processes. Their versatility extends beyond manufacturing into various industries, enhancing human-machine cooperation in roles like quality inspection and craftsmanship.
Additionally, there are robotic production lines that, as is the case for the ESSERT MicroFactory, allow the integration of a manual workstation, complementing the otherwise automated manufacturing process.
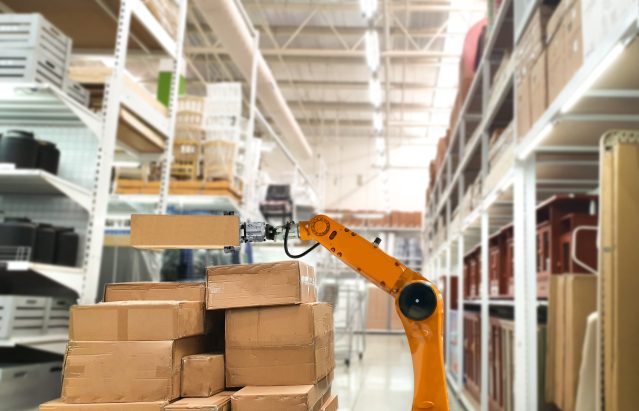
Mobile robots
The advent of autonomous mobile robots marks a paradigm shift in logistics and beyond. These intelligent machines navigate spaces with agility, driven by cutting-edge technologies like simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM).
Beyond the expected applications in warehouses, mobile robots are also revolutionizing fields like healthcare delivery within hospitals, streamlining the movement of supplies, and enhancing the overall efficiency of medical operations.
Additional types of robots
Apart from the aforementioned three main categories of robotics, there are several other types to distinguish. Some overlap, while others may also be seen as subtypes of a larger group of robotics. And while the following list does not claim to be exhaustive or universally applicable either, it does contain major types of robotics that manufacturers ought to know about.
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs)
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) push robotic independence to a new level. These intelligent machines navigate complex environments with a level of autonomy that goes beyond traditional mobile robots, such as Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).
AMRs find their footing in logistics, automating material transport in warehouses and manufacturing facilities. They adapt to dynamic surroundings, optimizing efficiency and reducing the need for fixed infrastructure.
Service robots
Service robots emerge as versatile entities designed to assist humans in various domains. From hospitality to healthcare, these robots take on roles that enhance customer service and streamline operations.
In hotels, service robots may deliver room service, while in healthcare settings, they support tasks like medication delivery, allowing human staff to focus on more intricate care.
Nanorobots
At the microscopic scale, nanorobots showcase the convergence of robotics and nanotechnology, making them a fascinating field of research.
The concept of nanorobots (a considerable part of which is still theoretical) includes minute robots operating within the human body, delivering targeted medical treatments and performing delicate procedures at the cellular level. In medicine, nanorobots hold promise for precise drug delivery, cancer treatment, and delicate surgical interventions.1
Humanoid robots
Humanoid robots bridge the gap between machines and humans, mimicking human form and movements. Beyond their roles in entertainment and research, humanoid robots contribute to industries like healthcare, where they assist in patient care and rehabilitation. Their anthropomorphic design allows for intuitive interaction and a wide range of robotic applications.
Educational robots
Enhancing interactive learning experiences, educational robots emerge as popular tools within academia. These robots, integrated seamlessly into classrooms, serve as engaging facilitators for teaching programming, robotics, and STEM subjects. Their presence catalyzes hands-on learning, providing students with practical insights into the technological landscapes that shape our future.
Medical robots
The medical field embraces specialized robots designed to augment healthcare delivery. Surgical robots, for example, can aid surgeons in performing complicated interventions that require an enhanced level of precision. Telepresence robots facilitate remote consultations, connecting patients and healthcare professionals seamlessly.
The integration of medical robots enhances diagnostics, surgeries, and patient care, advancing the frontiers of medical technology.
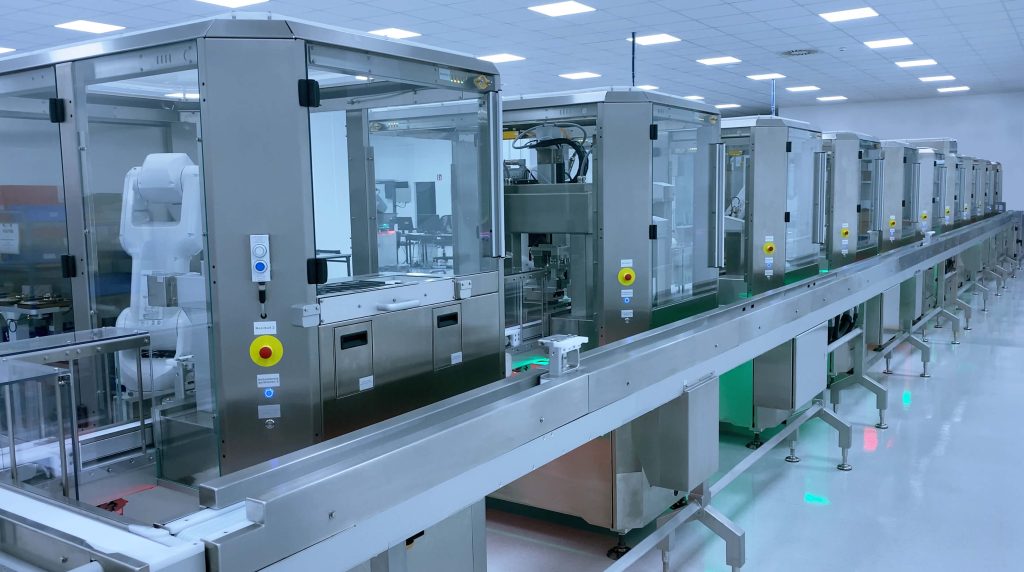

ESSERT Robotics – modular systems for various occasions
ESSERT Robotics leads the charge in adaptive automation solutions with its flagship products – the ADVANCED Robotic Workstation and the ESSERT MicroFactory.
The ADVANCED Robotic Workstation, marked by precision and flexibility, caters to diverse industries, including the pharmaceutical industry, offering a versatile platform for manufacturing processes. Its modular architecture facilitates seamless integration of various process modules, ensuring adaptability for high mix / low volume production. Notably, its stainless steel construction aligns with GMP standards, rendering it suitable for cleanroom applications as encountered in fields like medical device assembly.
The ESSERT MicroFactory takes versatility to new heights, offering a smart, modular, and scalable production line. This scalable system allows for quick and easy reconfiguration, accommodating a wide range of products with minimal effort. With advantages like flexible composition, independent commissioning, and plug-and-produce capability, the ESSERT MicroFactory emerges as a game-changer in the landscape of automated production, empowering industries to meet dynamic demands with unparalleled efficiency.
Read more about robotics
Robots in manufacturing: revolutionizing production processes
Robotic manufacturing companies
Cobot – all you need to know about collaborative robots
What is an industrial robot?
Robotics in the pharmaceutical industry
Robotics – 7 facts you need to know
- Oppermann, Artem. “What is nanorobotics?”. Buillt In, 03/2023. https://builtin.com/robotics/nanorobotics ↩︎