Pharmaceutical Automation: Innovations Shaping an Industry
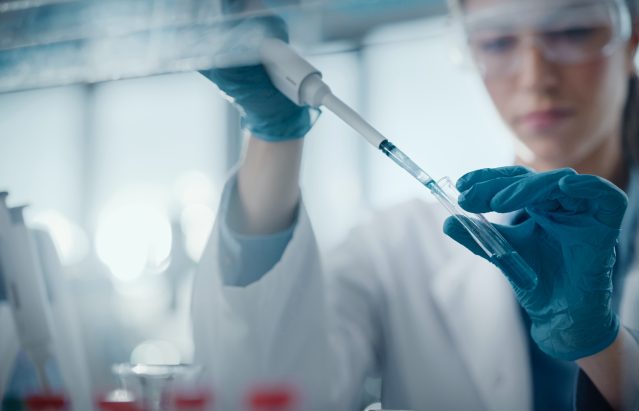

Pharmaceutical automation refers to the use of automated systems and technologies to streamline and enhance various processes within the pharmaceutical industry. These systems are designed to perform tasks such as drug discovery, packaging, quality control, inventory management, and distribution with minimal human intervention.
Considering the manifold processing steps that – especially in High Mix / Low Volume (HMLV) production – change on a regular basis, flexibility of the implemented automation solutions is key: Traditional, rigid yet costly customized constrictions do not suffice in this environment, making it necessary to bring flexibility and modularity to all aspects of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
But what are those aspects? This article will illustrate fields in the pharmaceutical industry that profit from innovations in automation, and explores which type of pharmaceutical automation is respectively applied. But first, let us clarify what is meant by automation in the pharmaceutical industry.
What is pharmaceutical automation?
Pharmaceutical automation encompasses a wide range of technologies, including robotics, computerized systems, robotic process automation, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and advanced analytics. These technologies enable pharmaceutical companies to increase efficiency, reduce errors, improve product quality, ensure regulatory compliance, and accelerate time to clinical trials and ultimately time-to-market for new drugs.
Overall, pharmaceutical automation plays a crucial role in modernizing and optimizing the pharmaceutical industry, ultimately benefiting both manufacturers and consumers by making drug development and distribution faster, safer, and more cost-effective.
There are several kinds of automation used in the pharmaceutical industry. In this article, we will explore some of them, like automated drug manufacturing or lab automation.
Automated manufacturing of drug products
Automated manufacturing processes, facilitated by robotics, revolutionize scaled-up production in the pharmaceutical industry. Robots excel in tasks like precise filling, medical device assembly, and packaging, ensuring consistency and accuracy at high speeds.
These automated systems enhance productivity by executing repetitive tasks flawlessly, minimizing errors, and maintaining stringent quality control throughout the production line. Moreover, their adaptability allows seamless integration into various production stages, optimizing efficiency and enabling pharmaceutical companies to meet the escalating demand for medications while upholding superior quality standards.
Drug discovery profiting from automation
Drug discovery processes have experienced a transformative shift, benefiting immensely from automation. Through high-throughput screening and automated technologies, the once time-consuming and labor-intensive task of identifying potential drug candidates has been revolutionized.
Automation expedites this screening process, swiftly analyzing vast libraries of compounds to pinpoint promising candidates with unprecedented efficiency and accuracy. This streamlined approach not only accelerates the discovery phase but also empowers researchers to focus more extensively on refining and developing the most viable drug candidates for further investigation and potential market introduction of new therapeutics.
Lab automation to drive innovation in the pharma industry
Lab automation serves as a driver for innovation in the pharmaceutical industry by replacing manual tasks, including pipetting, dispensing, sample preparation, and assay development, with more efficient automated processes. By integrating automated technologies, laboratories streamline experimentation processes, significantly reducing human error and enhancing precision.
This substitution of manual tasks with automated systems not only expedites workflows but also amplifies the capacity for conducting numerous experiments and analyses simultaneously, thereby accelerating research and development cycles.
Laboratories equipped with automated platforms also enable seamless data collection, analysis, and storage, empowering researchers to focus more on interpreting results and driving groundbreaking discoveries rather than routine, repetitive tasks.
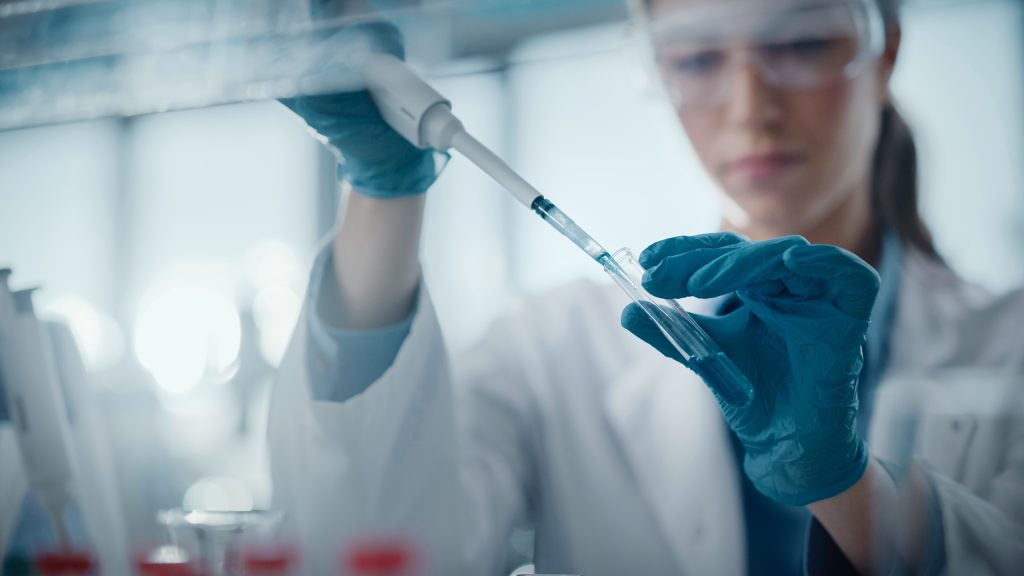

Automated quality control and data management
Automated quality control and real-time data management, encompassing both manufacturing automation powered by robots and software-based automation, fortify the pharmaceutical industry’s high standards.
The robots involved in automated manufacturing processes ensure consistent quality by standardizing inspection protocols and verifying products against predefined criteria. Combined with powerful software that navigates complex data sets, automation in quality control ensure accuracy in data entry, analysis, and compliance adherence.
These automated systems collectively expedite decision-making, flag anomalies swiftly, and maintain meticulous records, bolstering regulatory compliance and product integrity. Pharmaceutical companies can secure their operations, ensuring robust quality control and efficient data management across the production lifecycle.
Examples of automation in the pharmaceutical industry
Tasks in the pharmaceutical industry greatly benefit from automation, including:
Packaging and labeling:
Automation streamlines packaging of medical products, accurately labeling products and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Medical device assembly:
Automated assembly processes play a crucial role in the production of medical devices such as syringes, pens, and autoinjectors. Automated medical device assembly ensures precision and consistency in the composition of critical components, e.g. in syringe assembly.
Quality assurance testing:
Automated testing systems perform rigorous quality checks, ensuring products meet stringent quality standards – for example medical device testing.
Inventory management:
Automated systems track and manage stock levels, ensuring adequate supplies for uninterrupted production.
Compound synthesis:
Automated processes like automated pipetting facilitate precise and controlled synthesis of compounds, improving consistency and reducing error margins.
Logistics and distribution:
Automated systems optimize logistics, coordinating efficient distribution and timely delivery of pharmaceutical products.
Data analysis and reporting:
Automation aids in processing vast datasets, extracting insights, and generating comprehensive reports for informed decision-making.
Benefits of pharmaceutical automation
The advantages of pharmaceutical automation include:
- Enhanced efficiency: Automation streamlines processes such as drug manufacturing, packaging, and distribution, leading to lower downtime, increased productivity and faster production cycles.
- Improved quality control: Automated systems are capable of consistently monitoring and maintaining high-quality standards, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring the integrity of pharmaceutical products.
- Cost savings: Automation reduces the need for manual labor, minimizes waste, and optimizes resource utilization, resulting in cost savings for pharmaceutical companies.
- Regulatory compliance: Automated systems can help ensure compliance with stringent regulatory requirements by providing accurate documentation, traceability, and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
- Accelerated time-to-market: By expediting manufacturing processes and reducing lead times, automation enables pharmaceutical companies to bring new drugs to market more quickly, addressing patient needs faster.
- Increased safety: Automation reduces the potential for human errors, contamination, and exposure to hazardous materials, thereby enhancing safety for workers and consumers alike.
- Data-driven decision making: Automated systems generate vast amounts of data that can be analyzed to identify trends, optimize processes, and make informed strategic decisions, leading to continuous improvement and innovation within the pharmaceutical industry.
Overall, pharmaceutical automation offers numerous benefits that contribute to a more efficient, cost-effective, and reliable drug manufacturing and distribution ecosystem.
Automating pharmaceutical processes with ESSERT Robotics
It is the goal of ESSERT Robotics to support researchers, healthcare providers and pharmaceutical companies to make their manufacturing processes more efficient, streamlined and traceable. And being convinced that there is no way around automation as a fuel for optimization in the life sciences sector, solutions like the ADVANCED Robotic Workstation have been developed.
This extremely flexible platform can be equipped with various process modules, allowing it to take over repetitive tasks like pipetting, mixing and dispensing or medical device assembly. It is able to seamlessly collaborate with human workforces, but is also fully scalable, as multiple ADVANCED Robotic Workstations can be assembled to an ESSERT MicroFactory.
Each of the multiple ADVANCED Robotic Workstations forming the ESSERT MicroFactory carries out distinct production steps. This results in an entire HMLV production workflow that can easily be adapted to changing production requirements. The platform’s flexibility, combined with robotic precision and consistency, helps the pharmaceutical industry to fully benefit from the huge potential that automation has to offer.
FAQs about pharmaceutical automation
What is automation in the pharma industry?
What is the role of automation in the pharmaceutical industry?
What are examples of pharmaceutical automation?
Read more about automation in the pharmaceutical industry:
Robotics in the pharmaceutical industry
Pharma process automation: 5 reasons why it increases efficiency
Process automation simply explained
Pharmaceutical automation companies: Top 10 suppliers you should know
3 trends driving automation in life science industry
What is lab automation?
High-Mix Low-Volume: Possibilities & Limitations